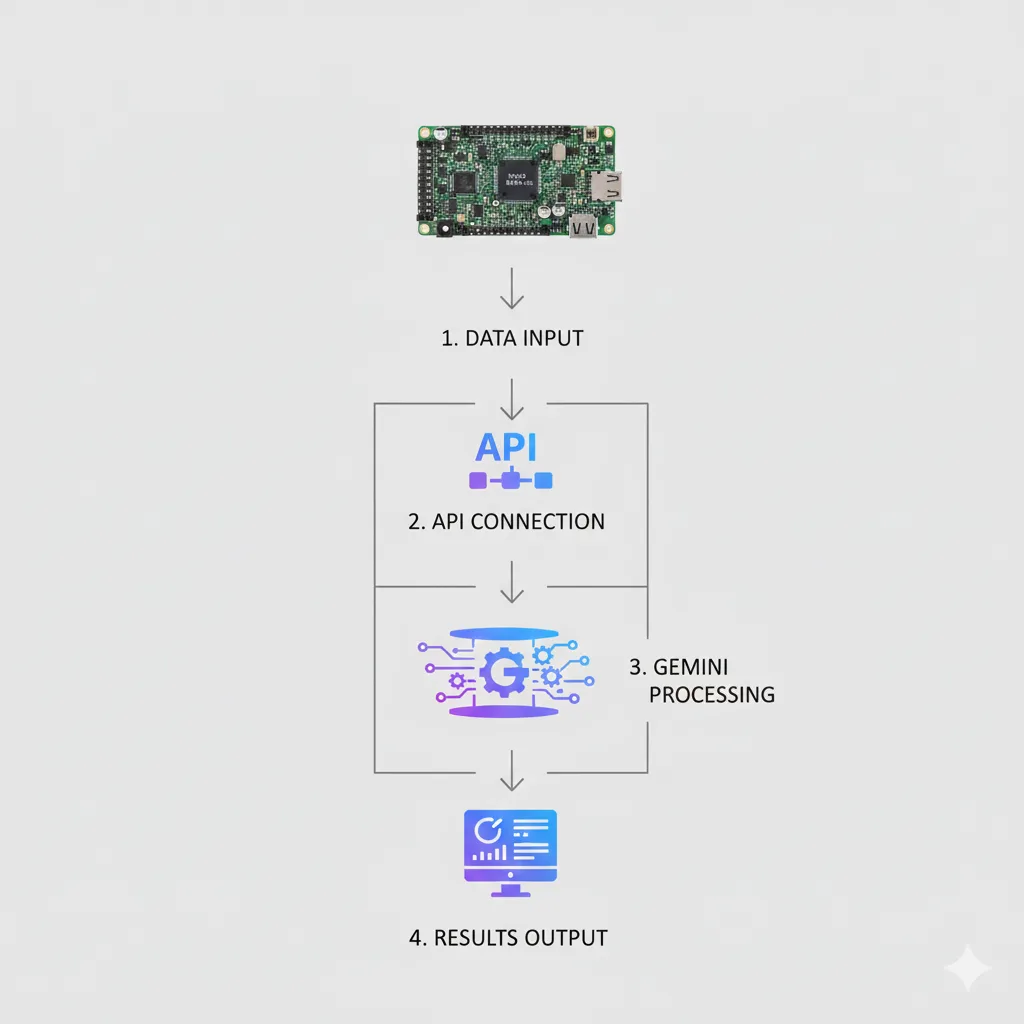
The integration of compact hardware solutions with advanced AI models has opened new possibilities for developers and tech enthusiasts. Nano Banana boards, combined with Google’s powerful Gemini AI model, create an exciting opportunity to build intelligent applications on edge devices. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about using Nano Banana with Google Gemini, from initial setup to advanced implementations.
Understanding Nano Banana
Nano Banana refers to compact single-board computers similar to Raspberry Pi or other SBC (Single Board Computer) platforms. These devices are characterized by their small form factor, low power consumption, and sufficient computing capabilities to run various applications. The “Banana” naming convention typically refers to boards in the Banana Pi family or similar alternatives that offer ARM-based processors, GPIO pins, and connectivity options like WiFi and Bluetooth.
These boards are ideal for edge computing applications where you need to process data locally without constantly relying on cloud services. When combined with AI capabilities, they become powerful tools for creating smart devices, IoT applications, and automated systems.
What is Google Gemini?
Google Gemini is Google’s advanced multimodal AI model that can understand and process text, images, audio, video, and code. Gemini comes in different versions optimized for various use cases, from the powerful Gemini Ultra to the more efficient Gemini Nano, which is specifically designed for on-device applications.
For Nano Banana implementations, you’ll typically interact with Gemini through Google’s API, which allows you to send requests and receive AI-generated responses. The API supports various tasks including natural language understanding, image analysis, code generation, and complex reasoning.
Prerequisites
Before you begin integrating Nano Banana with Google Gemini, ensure you have the following:
Hardware Requirements
- A Nano Banana board or similar SBC with at least 2GB RAM
- MicroSD card (16GB or larger recommended)
- Power supply compatible with your board
- Internet connectivity (WiFi or Ethernet)
- Optional: Camera module, sensors, or other peripherals depending on your project
Software Requirements
- Operating system installed on your Nano Banana (typically a Linux distribution)
- Python 3.7 or higher
- pip package manager
- Google Cloud account with Gemini API access
Account Setup
- Create a Google Cloud account if you don’t have one
- Enable the Gemini API in your Google Cloud Console
- Generate an API key for authentication
- Set up billing (though free tier options are available)
Setting Up Your Nano Banana
Initial Configuration
Start by ensuring your Nano Banana board is properly configured with the latest operating system. Most boards work well with Debian-based distributions like Armbian or Ubuntu. Flash the OS to your microSD card using tools like Etcher or dd command.
Once booted, update your system packages:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -y
Install essential development tools:
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-dev git build-essential
Installing Required Libraries
Install the Google Generative AI library for Python:
pip3 install google-generativeai
You may also want to install additional useful libraries:
pip3 install requests pillow python-dotenv
Configuring API Access
Create a configuration file to securely store your API key. Never hardcode API keys directly in your scripts. Use environment variables or configuration files with proper permissions:
nano ~/.gemini_config
Add your API key to this file and set appropriate permissions:
chmod 600 ~/.gemini_config
Basic Implementation
Simple Text Generation
Start with a basic script to test the connection. Create a Python file that imports the necessary libraries, sets up authentication, and makes a simple request to Gemini:
The basic workflow involves initializing the model with your API key, creating a prompt, sending the request, and processing the response. The Gemini API handles the heavy computational work in Google’s cloud infrastructure, while your Nano Banana simply sends requests and receives results.
Adding Image Analysis
One of Gemini’s powerful features is multimodal understanding. You can send images along with text prompts. This is particularly useful for projects involving camera modules. The board can capture images using a connected camera, encode them appropriately, and send them to Gemini for analysis.
The image processing workflow typically involves capturing an image using your camera module, converting it to the required format, combining it with a text prompt, and sending both to the API for analysis.
Advanced Use Cases
Building an Intelligent Camera System
Combine your Nano Banana with a camera module to create a smart surveillance system. The board can continuously capture images at intervals, analyze them using Gemini to detect specific objects or events, and trigger actions based on the analysis results.
This system could identify when packages are delivered, detect wildlife in your garden, or monitor for security concerns. The edge device handles image capture and basic preprocessing, while Gemini provides sophisticated understanding of what’s in the images.
Creating a Voice-Activated Assistant
Integrate speech recognition with Gemini to build a voice assistant. Use libraries like SpeechRecognition to convert voice to text, send the text to Gemini for processing, and use text-to-speech to deliver responses. This creates an interactive device that can answer questions, control smart home devices, or provide information.
IoT Data Analysis
Connect sensors to your Nano Banana and use Gemini to analyze the data intelligently. For example, environmental sensors could provide temperature, humidity, and air quality data. Gemini can analyze patterns, provide insights, and suggest actions based on the readings.
Educational Projects
Build interactive learning tools where students can ask questions and receive explanations. Point a camera at homework problems, send them to Gemini, and receive step-by-step solutions. This combines hardware interaction with AI-powered tutoring.
Optimization Strategies
Managing API Costs
Since Gemini API calls may incur costs, implement smart caching strategies. Store frequently asked questions and their responses locally. Only make API calls when necessary, such as when new or significantly different inputs are detected.
Improving Response Times
Minimize latency by preprocessing data on the Nano Banana before sending it to the API. Resize images to appropriate dimensions, compress data when possible, and structure your prompts efficiently to reduce processing time.
Power Efficiency
For battery-powered projects, implement sleep modes where the board only wakes up periodically or when triggered by specific events. This conserves power while maintaining functionality.
Error Handling
Implement robust error handling for network issues, API failures, or unexpected responses. Create fallback mechanisms and retry logic to ensure your application remains stable even when connectivity is unreliable.
Security Considerations
When working with API keys and potentially sensitive data, prioritize security. Never expose your API keys in public repositories. Use encrypted storage for credentials. If your device processes personal or sensitive information, ensure data is transmitted securely using HTTPS and consider encrypting data at rest.
Regularly update your Nano Banana’s operating system and all installed packages to patch security vulnerabilities. Implement authentication if your device is accessible over a network.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Connection Problems
If your Nano Banana can’t reach the Gemini API, verify internet connectivity first. Check firewall settings that might block outgoing requests. Ensure your API key is valid and has the necessary permissions.
Performance Bottlenecks
If responses are slow, examine your network connection quality. Large images or complex prompts take longer to process. Consider preprocessing data more aggressively or using smaller input sizes.
Memory Constraints
Nano Banana boards have limited RAM compared to desktop computers. Monitor memory usage and optimize your code to avoid memory leaks. Process data in smaller chunks if needed.
Conclusion
Combining Nano Banana boards with Google Gemini creates powerful possibilities for edge AI applications. The compact hardware handles local processing and data collection, while Gemini provides sophisticated AI capabilities through the cloud. This architecture allows you to build intelligent devices that are both responsive and capable of complex understanding.
Whether you’re creating smart home devices, educational tools, or innovative IoT solutions, this combination offers flexibility and power. Start with simple projects to understand the workflow, then gradually expand to more complex applications as you become comfortable with both the hardware and API.
The future of edge computing lies in exactly this kind of integration—bringing advanced AI capabilities to small, efficient devices that can operate independently while still accessing cloud-based intelligence when needed. Your Nano Banana with Gemini integration is a step into this exciting future of distributed, intelligent computing.